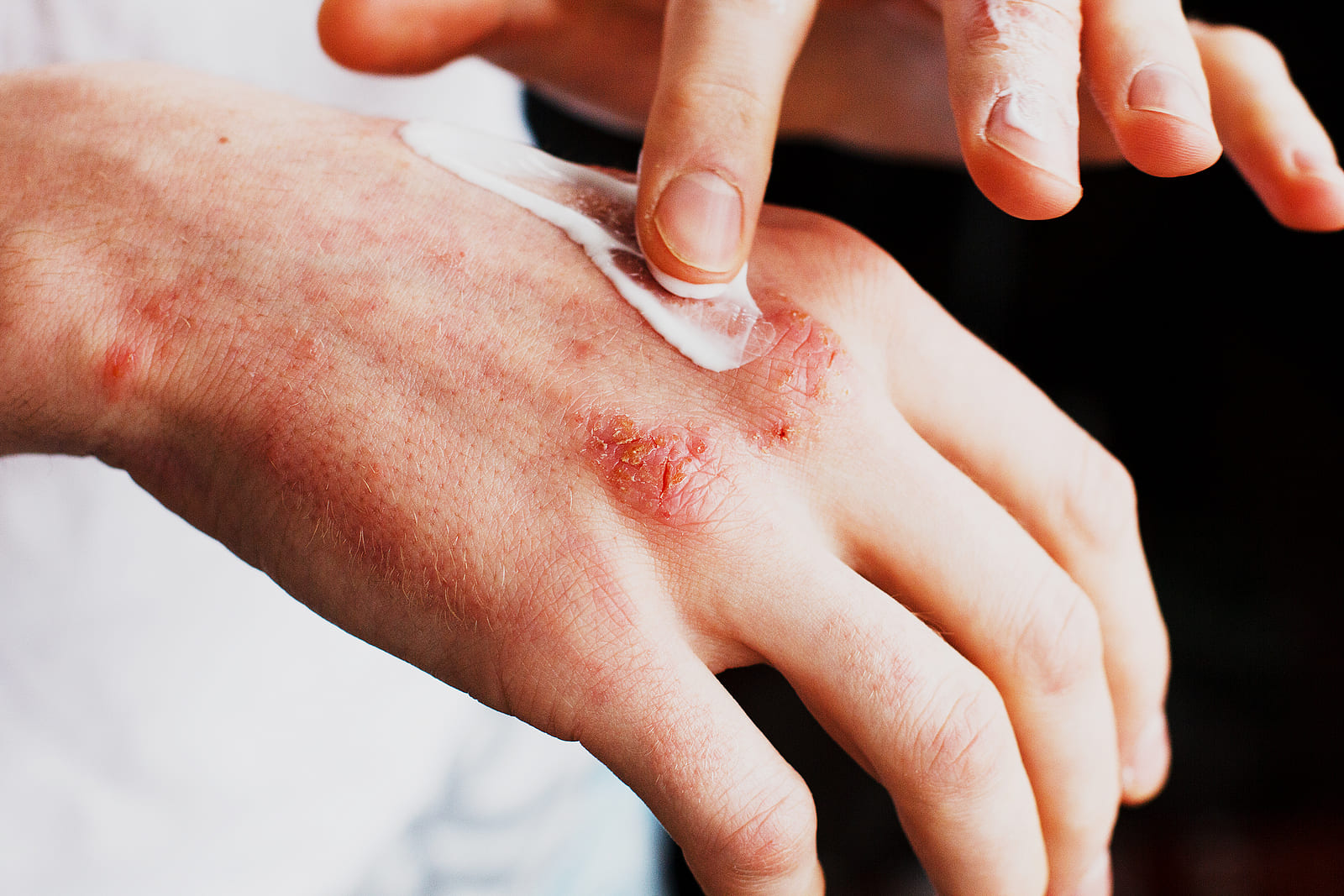
Atopic Dermatitis (Eczema)


Bare Dermatology is proud to announce the launch of the Eczema Institute of North Texas, a new specialized center dedicated to providing comprehensive care for individuals suffering from eczema and other related skin conditions. The institute aims to bring cutting-edge treatments, personalized care, and expert guidance to the North Texas community, helping patients manage and overcome the challenges posed by eczema. With a focus on innovative therapies and a team of experienced dermatologists, the Eczema Institute is committed to improving the quality of life for those affected by this common, yet often debilitating, condition.
Overview
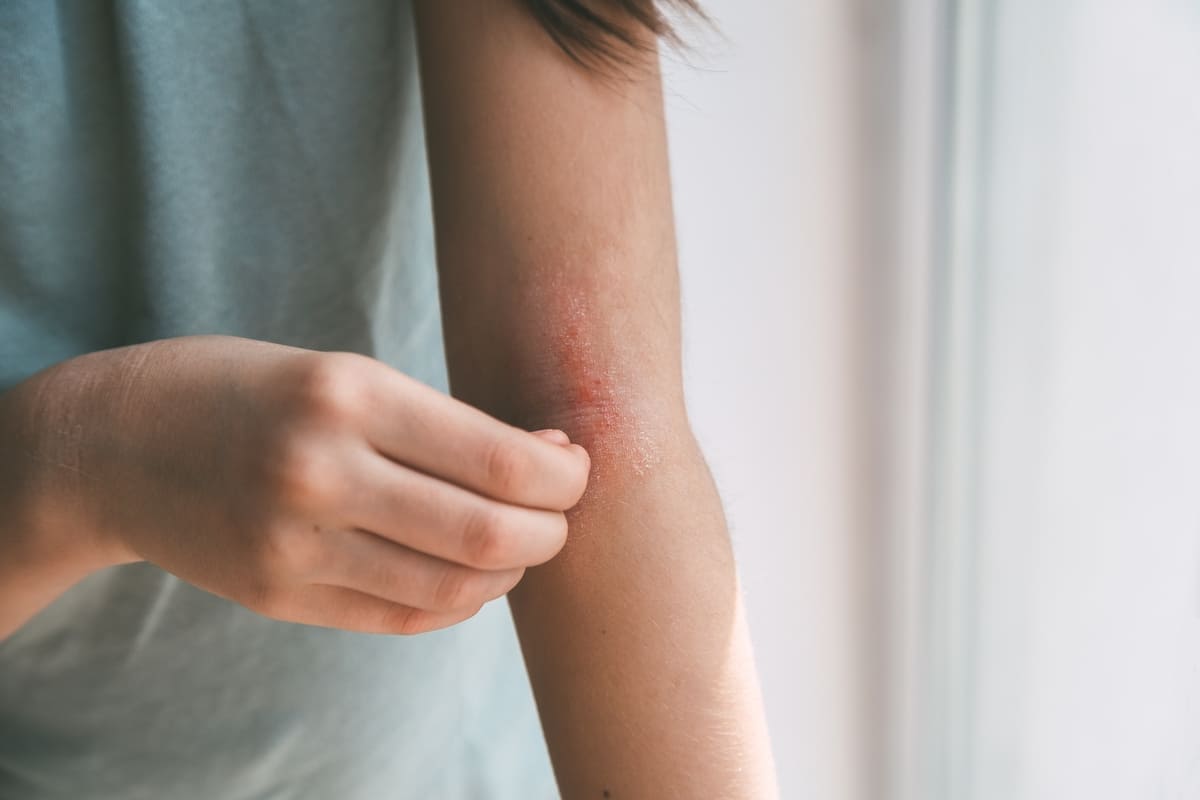
Eczema is an inflammatory skin condition that causes dry skin, itching, and rashes. There are 7 different types of eczema, and more than 31 million Americans have some form of eczema. Eczema commonly starts in childhood but can occur at any age. The exact cause of eczema is unknown, but genetics and environmental triggers are understood to play a role.